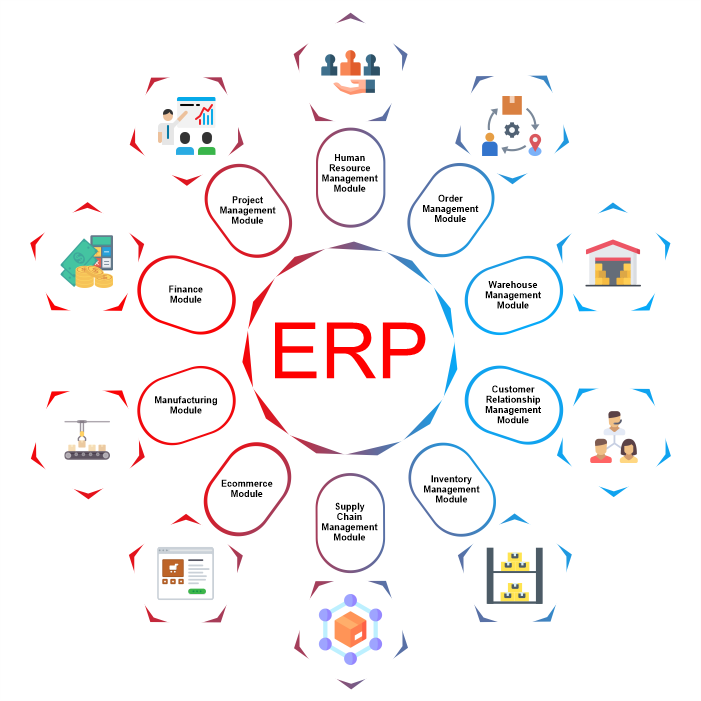
Different Modules of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Now days ERP software is become an important aspect for many businesses to manage their company’s resources. An ERP system optimizes critical business processes and serves as the organization's single repository for all operational and financial data. It gathers this data using a number of modules designed to help various departments—including accounting, supply chain, and human resources—perform their specific tasks. Due to its great degree of adaptability, ERP is a desirable and adaptable solution for a variety of operations. Each module puts data into the main database after pulling it from particular business sectors. Decision-makers can use this to compare and assess the state of various business sectors.
Here are some ERP software's main modules:
1. Human Resource Management Module: In addition to offering more capability, a human resource management (HRM) module frequently contains all the elements of a workforce management program. It's one of the most frequently used modules of ERP because it offers so much useful data and procedures. Managers may access entire personnel information using the HR ERP module, ensuring that the correct individual is placed in the proper position. The HR module's payroll system aids in managing salaries, payment reports, and other financial matters. ERP can be utilized to track staff training as well. Since the HRM module keeps a variety of information on each employee across the organization, it eliminates a significant amount of unnecessary or inaccurate data that many businesses save in separate spreadsheets.
2. Order Management Module: Orders are tracked via an order management module from arrival to delivery. As they are delivered to customers, it monitors their progress. By doing this, orders are delivered promptly, and none are misplaced. In order to keep customers happy and reduce unnecessary costs for expedited shipping, the order management module reduces order loss and increases on-time delivery rates. A business can choose the most cost-effective method of order fulfilment, such as a store, warehouse, or third-party fulfilment partner, based on the stock that is currently available and the location of the buyer, with the help of more sophisticated order management tools.
3. Ware House Management Module: High-volume warehouse operations are managed by warehouse management module, which also directs workers through every step of the process—from putting things away to picking, packaging, and shipping. A warehouse management system may provide a quick return on investment for companies with their own storage facilities. The warehouse management module can handle a variety of picking strategies, including batch picking, wave picking, and zone picking, depending on which is most advantageous for a given company. Some modules can even show staff the most effective picking path.
4. Customer Relationship Management Module: The customer relationship management module has emerged as one of the most crucial ERP modules as a result of the expanding impact of customers in business activities. The main goal of the CRM module is to boost sales performance by offering clients a comprehensive experience and customer care. This includes both the customer's past purchases and the business's record of correspondence with them. These modules contain contact lists, interaction histories, and core analytics as some of the fundamental CRM capabilities. The CRM department helps to boost sales success by offering top-notch customer service and developing strong relationships with clients.
5. Inventory Management Module: The inventory management module enables inventory control, which maintains track of the quantity of things and their locations. It enables firms to get real-time inventory data and control every part of their operations from a single location. Stock utilization reporting, master units, and inventory control are some of the functions available in the inventory module. They are involved from the point of acquisition to the final delivery notice, and they endeavour to maximize productivity through the management of sales orders, shipping, and invoices. Some of the general advantages of this technology include higher profit margins, more efficiency, and happier consumers.
6. Supply Chain Management Module: A supply chain management module keeps track of each stage of the flow of supplies and products from sub-suppliers through suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and customers. It may manage the return of any materials or products for a refund or a replacement. It assists in making sure there is sufficient inventory supply, preventing shortages during the production process. It gathers and examines customer data, forecasts the kinds of customer campaigns that will have the biggest impact.
7. Ecommerce Module: Manufacturers can access a feature-rich ecommerce platform through an integrated ecommerce module with ERP software. The best e-commerce software offers intuitive features that make it simple for staff members to add new items, change product information (descriptions, names, specifications, photographs, etc.), and change the look and feel of the website. When connected to other ERP programs, the e-commerce module transfers all transaction, purchase, and inventory data into the shared database. This ensures that every transaction is tracked in the database that items that are out of stock are removed from the website and that shipments are made on time.
8. Manufacturing: ERP still includes manufacturing as a key component. Programs for material requirements planning (MRP), the earliest version of ERP, were created for manufacturers. The manufacturing module helps producers plan their output and make sure they have the capacity and raw materials necessary for planned production runs. It can be used to compare actual output to predicted output and to update the status of goods-in-progress during the manufacturing process. Accurate information regarding the production cycle is tracked, gathered, and monitored by the Manufacturing Execution System. It encourages data gathering, product tracking, and resource and quality control management.
9. Finance Module: The ERP finance module is one of the key modules. It supports various accounting functions such as ledger administration, billing, vendor payments, cash management, bank reconciliation, etc., as well as the management of all cash inflows and outflows. The implementation of financial management capabilities in your ERP platform is undoubtedly one of the most useful and in-demand features. Additionally, it contains the information that employees in financial planning and analysis need to run scenario plans and generate important reports, such as profit and loss (P&L) statements and board reports.
10. Project Management Module: With the use of the project management module, the business may manage all of its projects and their associated details. It also keeps track of all the activities and makes sure they don't take longer than scheduled. It enables managers to control personnel and financial resources while monitoring project progress and approving expenses and timesheets. It encourages team cooperation by putting all relevant documents in a central location.
Conclusion:
By organizing all client data, including contact information, order history, and support issues, an ERP enables organizations to enhance customer service. This allows for speedier solutions and a more individualized experience when customers do need support. It is difficult to develop custom ERP software that works effectively and efficiently while increasing productivity in any business.
A variety of customers have benefited from Career IT and Business Solutions' customized ERP software solutions and their excellent after-sales service. It is a reputed ERP software development company in Edmonton, Canada.
